1 数据说明
-
LANDSAT/LC8_L1T_TOA
-
详细的说明可以看注释
2 结果展示
线性和非线性拟合
| 线性 | 非线性 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
滑动平均值
| 原始值 | 滑动平均值 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
3 详细代码
var l8toa = ee.ImageCollection("LANDSAT/LC8_L1T_TOA");
var roi = ee.Geometry.Point([-121.9353461265564, 37.56180984982223]);
Map.centerObject(roi, 10);
// This field contains UNIX time in milliseconds.
var timeField = 'system:time_start';
// Use this function to mask clouds in Landsat 8 imagery.
var maskClouds = function(image) {
var quality = image.select('BQA');
var cloud01 = quality.eq(61440);
var cloud02 = quality.eq(53248);
var cloud03 = quality.eq(28672);
var mask = cloud01.or(cloud02).or(cloud03).not();
return image.updateMask(mask);
};
// Use this function to add variables for NDVI, time and a constant
// to Landsat 8 imagery.
var addVariables = function(image) {
// Compute time in fractional years since the epoch.
var date = ee.Date(image.get(timeField));
var years = date.difference(ee.Date('1970-01-01'), 'year');
// Return the image with the added bands.
return image
// Add an NDVI band.
.addBands(image.normalizedDifference(['B5', 'B4']).rename('NDVI')).float()
// Add a time band.
.addBands(ee.Image(years).rename('t').float())
// Add a constant band.
.addBands(ee.Image.constant(1));
};
// Remove clouds, add variables and filter to the area of interest.
var filteredLandsat = l8toa
.filterBounds(roi)
.map(maskClouds)
.map(addVariables);
// Plot a time series of NDVI at a single location.
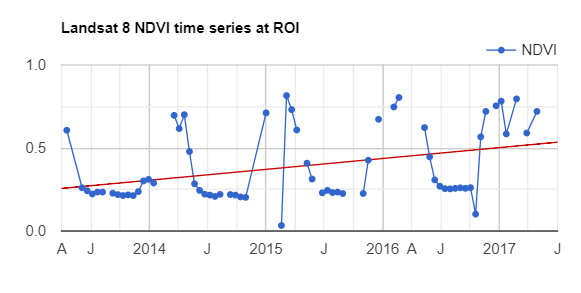
var l8Chart = ui.Chart.image.series(filteredLandsat.select('NDVI'), roi)
.setChartType('ScatterChart')
.setOptions({
title: 'Landsat 8 NDVI time series at ROI',
trendlines: {0: {
color: 'CC0000'
}},
lineWidth: 1,
pointSize: 3,
});
print(l8Chart);
// Linear trend ----------------------------------------------------------------
// List of the independent variable names
var independents = ee.List(['constant', 't']);
// Name of the dependent variable.
var dependent = ee.String('NDVI');
// Compute a linear trend. This will have two bands: 'residuals' and
// a 2x1 band called coefficients (columns are for dependent variables).
var trend = filteredLandsat.select(independents.add(dependent))
.reduce(ee.Reducer.linearRegression(independents.length(), 1));
// Map.addLayer(trend, {}, 'trend array image');
// Flatten the coefficients into a 2-band image
var coefficients = trend.select('coefficients')
.arrayProject([0])
.arrayFlatten([independents]);
// Compute a de-trended series.
var detrended = filteredLandsat.map(function(image) {
return image.select(dependent).subtract(
image.select(independents).multiply(coefficients).reduce('sum'))
.rename(dependent)
.copyProperties(image, [timeField]);
});
// Plot the detrended results.
var detrendedChart = ui.Chart.image.series(detrended, roi, null, 30)
.setOptions({
title: 'Detrended Landsat time series at ROI',
lineWidth: 1,
pointSize: 3,
});
print(detrendedChart);
// Harmonic trend ----------------------------------------------------------------
// Use these independent variables in the harmonic regression.
var harmonicIndependents = ee.List(['constant', 't', 'cos', 'sin']);
// Add harmonic terms as new image bands.
var harmonicLandsat = filteredLandsat.map(function(image) {
var timeRadians = image.select('t').multiply(2 * Math.PI);
return image
.addBands(timeRadians.cos().rename('cos'))
.addBands(timeRadians.sin().rename('sin'));
});
// The output of the regression reduction is a 4x1 array image.
var harmonicTrend = harmonicLandsat
.select(harmonicIndependents.add(dependent))
.reduce(ee.Reducer.linearRegression(harmonicIndependents.length(), 1));
// Turn the array image into a multi-band image of coefficients.
var harmonicTrendCoefficients = harmonicTrend.select('coefficients')
.arrayProject([0])
.arrayFlatten([harmonicIndependents]);
// Compute fitted values.
var fittedHarmonic = harmonicLandsat.map(function(image) {
return image.addBands(
image.select(harmonicIndependents)
.multiply(harmonicTrendCoefficients)
.reduce('sum')
.rename('fitted'));
});
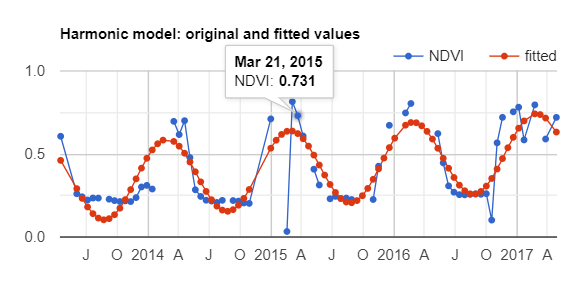
// Plot the fitted model and the original data at the ROI.
print(ui.Chart.image.series(
fittedHarmonic.select(['fitted','NDVI']), roi, ee.Reducer.mean(), 30)
.setSeriesNames(['NDVI', 'fitted'])
.setOptions({
title: 'Harmonic model: original and fitted values',
lineWidth: 1,
pointSize: 3,
}));
// Compute phase and amplitude.
var phase = harmonicTrendCoefficients.select('cos').atan2(
harmonicTrendCoefficients.select('sin'));
var amplitude = harmonicTrendCoefficients.select('cos').hypot(
harmonicTrendCoefficients.select('sin'));
// Use the HSV to RGB transform to display phase and amplitude
var rgb = phase.unitScale(-Math.PI, Math.PI).addBands(
amplitude.multiply(2.5)).addBands(
ee.Image(1)).hsvToRgb();
Map.addLayer(rgb, {}, 'phase (hue), amplitude (saturation)');
// Autocovariance and autocorrelation ---------------------------------------------
// Function to get a lagged collection. Images that are within
// lagDays of image are stored in a List in the 'images' property.
var lag = function(leftCollection, rightCollection, lagDays) {
var filter = ee.Filter.and(
ee.Filter.maxDifference({
difference: 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * lagDays,
leftField: timeField,
rightField: timeField
}),
ee.Filter.greaterThan({
leftField: timeField,
rightField: timeField
}));
return ee.Join.saveAll({
matchesKey: 'images',
measureKey: 'delta_t',
ordering: timeField,
ascending: false, // Sort reverse chronologically
}).apply({
primary: leftCollection,
secondary: rightCollection,
condition: filter
});
};
// Lag the Landsat series to get the previous image.
// Note that the results vary when using detrended data
var lagged17 = lag(detrended, detrended, 17);
print(lagged17,'lagged17 ')
// Function to merge bands of a lagged collection. If a collection is
// lagged with itself, the band names will be appended with an '_' and
// suffixed by an index of the order in which they were added. Because
// the 'images' list is sorted reverse chronologically, band_1 is the t-1
// image when the band names collide.
var merge = function(image) {
// Function to be passed to iterate.
var merger = function(current, previous) {
return ee.Image(previous).addBands(current);
};
return ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(image.get('images')).iterate(merger, image);
};
// Merge the bands together.
var merged17 = ee.ImageCollection(lagged17.map(merge));
// Function to compute covariance over time. This will return
// a 2x2 array image. Pixels contains variance-covariance matrices.
var covariance = function(mergedCollection, band, lagBand) {
return mergedCollection.select([band, lagBand]).map(function(image) {
return image.toArray();
}).reduce(ee.Reducer.covariance(), 8);
};
// Compute covariance from the merged series.
var lagBand = dependent.cat('_1');
var covariance17 = ee.Image(covariance(merged17, dependent, lagBand));
// (Note that covariance accentuates agriculture)
Map.addLayer(covariance17.arrayGet([0, 1]), {}, 'covariance (lag = 17 days)');
// Compute correlation from a 2x2 covariance image.
var correlation = function(vcArrayImage) {
var covariance = ee.Image(vcArrayImage).arrayGet([0, 1]);
var sd0 = ee.Image(vcArrayImage).arrayGet([0, 0]).sqrt();
var sd1 = ee.Image(vcArrayImage).arrayGet([1, 1]).sqrt();
return covariance.divide(sd0).divide(sd1).rename('correlation');
};
// Correlation
var correlation17 = correlation(covariance17);
// (Not sure what this means)
Map.addLayer(correlation17, {min: -1, max: 1}, 'correlation (lag = 17 days)');
// Lag the Landsat series to get the previous image.
var lagged34 = lag(detrended, detrended, 34);
// Merge the bands together.
var merged34 = ee.ImageCollection(lagged34.map(merge))
.map(function(image) {
return image.set('laggedImages', ee.List(image.get('images')).length());
})
.filter(ee.Filter.gt('laggedImages', 1));
// Compute covariance from the merged series.
var covariance34 = ee.Image(covariance(merged34, dependent, dependent.cat('_2')));
Map.addLayer(covariance34.arrayGet([0, 1]), {}, 'covariance34');
// Cross-correlation ----------------------------------------------------------------
// Precipitation (covariate)
var chirps = ee.ImageCollection('UCSB-CHG/CHIRPS/PENTAD');
// Join the precipitation images from a pentad ago
var lag1PrecipNDVI = lag(filteredLandsat, chirps, 5);
print('lag1PrecipNDVI', lag1PrecipNDVI);
// Add the precipitation images as bands.
var merged1PrecipNDVI = ee.ImageCollection(lag1PrecipNDVI.map(merge));
print('merged1PrecipNDVI', merged1PrecipNDVI);
// Compute covariance.
var cov1PrecipNDVI = covariance(merged1PrecipNDVI, 'NDVI', 'precipitation');
Map.addLayer(cov1PrecipNDVI.arrayGet([0, 1]), {}, 'NDVI - PRECIP cov (lag = 5)');
// Correlation.
var corr1PrecipNDVI = correlation(cov1PrecipNDVI);
Map.addLayer(corr1PrecipNDVI, {min: -0.5, max: 0.5}, 'NDVI - PRECIP corr (lag = 5)');
// Advanced cross-correlation----------------------------------------------------
// Join the precipitation images from the previous month
var lag30PrecipNDVI = lag(filteredLandsat, chirps, 30);
print(lag30PrecipNDVI);
var sum30PrecipNDVI = ee.ImageCollection(lag30PrecipNDVI.map(function(image) {
var laggedImages = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(image.get('images'));
return ee.Image(image).addBands(laggedImages.sum().rename('sum'));
}));
// Compute covariance.
var cov30PrecipNDVI = covariance(sum30PrecipNDVI, 'NDVI', 'sum');
Map.addLayer(cov1PrecipNDVI.arrayGet([0, 1]), {}, 'NDVI - sum cov (lag = 30)');
// Correlation.
var corr30PrecipNDVI = correlation(cov30PrecipNDVI);
Map.addLayer(corr30PrecipNDVI, {min: -0.5, max: 0.5}, 'NDVI - sum corr (lag = 30)');
// AR models --------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Lag the Landsat series to get the previous image.
var lagged34 = ee.ImageCollection(lag(filteredLandsat, filteredLandsat, 34));
// Merge the bands together.
var merged34 = lagged34.map(merge).map(function(image) {
return image.set('n', ee.List(image.get('images')).length());
}).filter(ee.Filter.gt('n', 1));
// These names are based on the default behavior of addBands(), which
// appends '_n' for the nth time the band name is replicated.
var arIndependents = ee.List(['constant', 'NDVI_1', 'NDVI_2']);
var ar2 = merged34
.select(arIndependents.add(dependent))
.reduce(ee.Reducer.linearRegression(arIndependents.length(), 1));
// Turn the array image into a multi-band image of coefficients.
var arCoefficients = ar2.select('coefficients')
.arrayProject([0])
.arrayFlatten([arIndependents]);
// Compute fitted values.
var fittedAR = merged34.map(function(image) {
return image.addBands(
image.expression('beta0 + beta1 * p1 + beta2 * p2', {
p1: image.select('NDVI_1'),
p2: image.select('NDVI_2'),
beta0: arCoefficients.select('constant'),
beta1: arCoefficients.select('NDVI_1'),
beta2: arCoefficients.select('NDVI_2')
}).rename('fitted'));
});
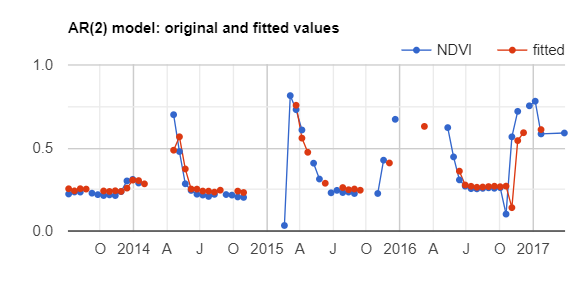
// Plot the fitted model and the original data at the ROI.
print(ui.Chart.image.series(
fittedAR.select(['fitted', 'NDVI']), roi, ee.Reducer.mean(), 30)
.setSeriesNames(['NDVI', 'fitted'])
.setOptions({
title: 'AR(2) model: original and fitted values',
lineWidth: 1,
pointSize: 3,
}));
// Forecasting
var fill = function(current, list) {
// Get the date of the last image in the list.
var latestDate = ee.Image(ee.List(list).get(-1)).date();
// Get the date of the current image being processed.
var currentDate = ee.Image(current).date();
// If those two dates are more than 16 days apart, there's
// a temporal gap in the sequence. To fill in the gap, compute
// the potential starting and ending dates of the gap.
var start = latestDate.advance(16, 'day').millis();
var end = currentDate.advance(-16, 'day').millis();
// Determine if the start and end dates are chronological.
var blankImages = ee.Algorithms.If({
// Watch out for this. Might need a tolerance here.
condition: start.lt(end),
// Make a sequence of dates to fill in with empty images.
trueCase: ee.List.sequence({
start: start,
end: end,
step: 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 16
}).map(function(date) {
// Return a dummy image with a masked NDVI band and a date.
return ee.Image(0).mask(0).rename('NDVI').set({
'dummy': true,
'system:time_start': ee.Date(date).millis()
});
}),
// If there's no gap, return an empty list.
falseCase: []
});
// Add any dummy images and the current image to the list.
return ee.List(list).cat(blankImages).add(current);
};
// The first image is the starting image.
var first = filteredLandsat.first();
// The first image is duplicated in this list, so slice it off.
var filled = ee.List(filteredLandsat.iterate(fill, [first])).slice(1);
// Now, map a function over this list to do the prediction.
var indices = ee.List.sequence(5, filled.length().subtract(1));
// A function to forecast from the previous two images.
var forecast = function(current, list) {
var ndvi = ee.Image(current).select('NDVI');
// Get the t-1 and t-2 images.
var size = ee.List(list).size();
var image1 = ee.Image(ee.List(list).get(size.subtract(1)));
var image2 = ee.Image(ee.List(list).get(size.subtract(2)));
var predicted = ee.Image().expression('beta0 + beta1 * p1 + beta2 * p2', {
p1: image1.select('NDVI'),
p2: image2.select('NDVI'),
beta0: arCoefficients.select('constant'),
beta1: arCoefficients.select('NDVI_1'),
beta2: arCoefficients.select('NDVI_2')
}).rename('NDVI')
.set('system:time_start', current.get('system:time_start'));
// Replace the entire image if it's a dummy.
var replaced = ee.Algorithms.If({
condition: current.get('dummy'),
trueCase: predicted,
// Otherwise replace only masked pixels.
falseCase: current.addBands({
srcImg: ndvi.unmask().where(ndvi.mask().not(), predicted).rename('NDVI'),
overwrite: true
})
});
// Add the predicted image to the list.
return ee.List(list).add(replaced);
};
// Start at a point in the sequence with three consecutive real images.
var startList = filled.slice(4, 5);
// Iterate over the filled series to replace dummy images with predictions.
var modeled = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(
ee.ImageCollection(filled).iterate(forecast, startList)).select('NDVI');
print(ui.Chart.image.series(
modeled, roi, ee.Reducer.mean(), 30)
.setSeriesNames(['NDVI'])
.setOptions({
title: 'forecast',
lineWidth: 1,
pointSize: 3,
}));
// Smoothing ---------------------------------------------------------------
var join = ee.Join.saveAll({
matchesKey: 'images'
});
var diffFilter = ee.Filter.maxDifference({
difference: 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 17,
leftField: timeField,
rightField: timeField
});
var threeNeighborJoin = join.apply({
primary: modeled,
secondary: modeled,
condition: diffFilter
});
var smoothed = ee.ImageCollection(threeNeighborJoin.map(function(image) {
var collection = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(image.get('images'));
return ee.Image(image).addBands(collection.mean().rename('mean'));
}));
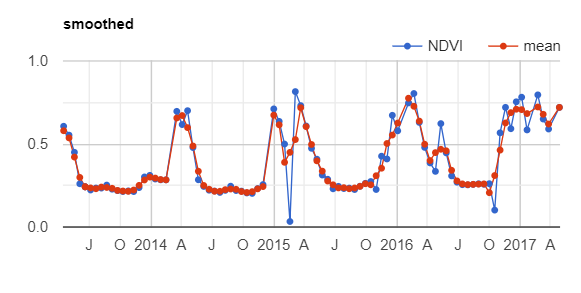
// Note that there is still a discontinuity in the chart. While there may be
// two neighbors, the pixel may be masked at one or all of those times.
print(ui.Chart.image.series(
smoothed.select(['NDVI', 'mean']), roi, ee.Reducer.mean(), 30)
.setSeriesNames(['NDVI', 'mean'])
.setOptions({
title: 'smoothed',
lineWidth: 1,
pointSize: 3,
}));